Customerlabs CDP Documentation
-
Getting Started
-
Core Concepts
-
Website Event Tracking
-
- E-commerce Platform Integration
- Shopify+CustomerLabs Integration Guide
- WooCommerce + CustomerLabs Integration Guide
- BigCommerce + CustomerLabs Integration Guide
- Custom conversion or synthetic events for Shopify and WooCommerce
- Hubspot + CustomerLabs integration
- Go High Level+ CustomerLabs Integration Tracking
- Typeform + CustomerLabs Integration Tracking
- Formstack + CustomerLabs Integration Tracking
-
-
-
Destinations
- CustomerLabs + Google Analytics (GA4) Integration
- CustomerLabs + Google Adwords Integration
- Customerlabs + Facebook Offline Conversion Integration
- CustomerLabs + Meta CRM Pixel Integration
- CustomerLabs + Intercom Integration
- CustomerLabs + iiintent.io Integration
- CustomerLabs + LinkedIn Integration
- CustomerLabs + Zapier Integration
- CustomerLabs + Drip Integration
- CustomerLabs + Segment Integration
- CustomerLabs + Google Sheets Integration
- CustomerLabs + Gist (ConvertFox) Integration
- CustomerLabs + Webhooks Integration
- CustomerLabs + BigQuery Integration
- CustomerLabs + Mixpanel Integration
- CustomerLabs + Customer.io integration
- CustomerLabs + Sendinblue Integration
- CustomerLabs + Klaviyo Integration
- CustomerLabs + TikTok Integration (Beta)
- CustomerLabs + Audience Lab Integration
- CustomerLabs + Maropost Integration
- CustomerLabs + LimeChat Integration
- CustomerLabs + KickBox Integration
- CustomerLabs + Snapchat Integration
- Show all articles ( 14 ) Collapse Articles
-
Sources
- Introduction to CustomerLabs Sources
- Source - Freshsales
- Source - HubSpot
- Source - Drift
- Source - Intercom
- Source - Facebook
- Source – Salesforce
- Source - iiintent.io
- Custom Source
- Source - CSV Upload
- Source - Pipedrive
- Source - Jotform
- Source - Typeform
- Source - Google Ads
- Show all articles ( 4 ) Collapse Articles
-
Segmentation
-
Monitoring
-
Privacy
-
Help
-
Change Log
-
Custom Branding
Setting up URL patterns using Regex
You can choose on which pages the captured event should or should not fire. The common options include the current or all pages.
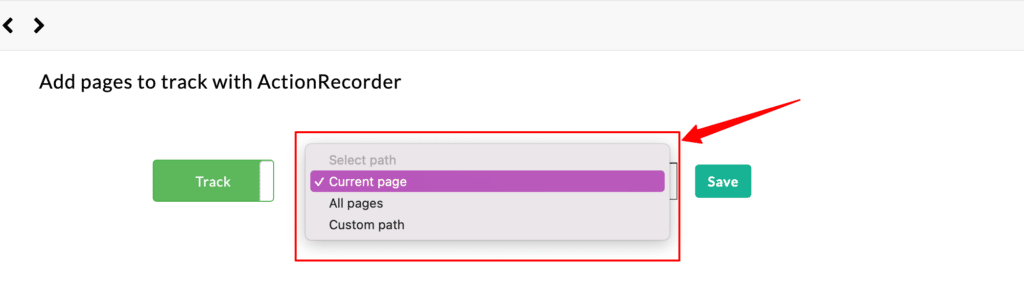
You can also a custom URL path. Here are some scenarios where this option will come in handy.
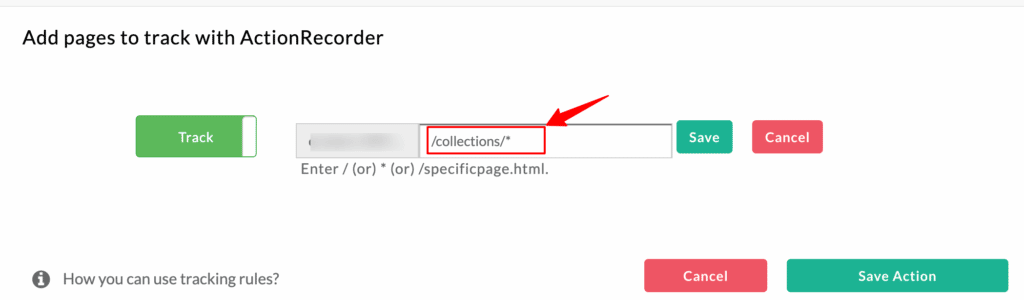
Case 1: If your desired tracking path is at the beginning
For the following example, add a ( /* ) symbol after collections. This means we will track all pages after collections, irrespective of the URL text present after it.
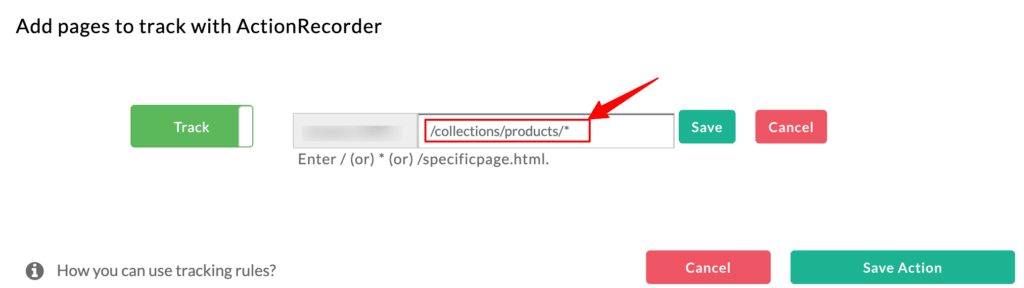
Case 2: If your desired tracking path is at the centre
Let’s try it with the different scenario where if the desired path for tracking is present in between 2nd and 3rd “/” (eg: products)
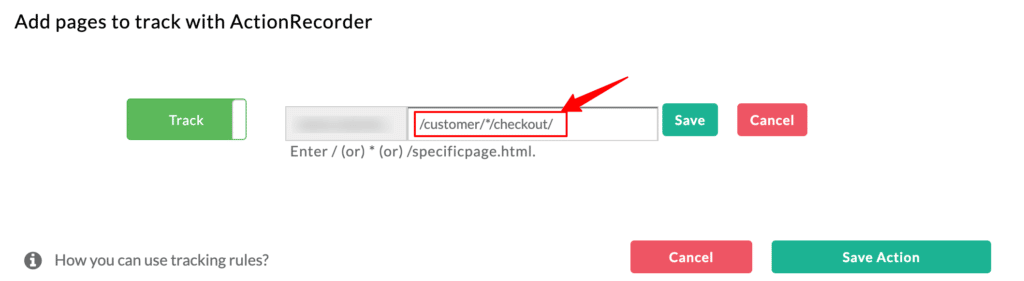
Case 3: If your desired tracking path is a dynamic variable
Let’s try a different case, where if you want to track the customer ID. By adding (customer/*/checkout), defines customer and the checkout as the static variable (which doesn’t change). Usually, ID differs from each customer. So by adding (*) in the centre represents value or the variable as a dynamic path (Differs from customer to customer).
0 out Of 5 Stars
| 5 Stars | 0% | |
| 4 Stars | 0% | |
| 3 Stars | 0% | |
| 2 Stars | 0% | |
| 1 Stars | 0% |



