Are you still relying on cookies to target your audience? With new privacy laws and browsers blocking third-party cookies, marketers are scrambling to find alternatives. As cookies fade out, your business may need to rethink its ad strategies—especially when it comes to privacy and personalization. Let’s take a look at some key stats to understand the impact of this shift.
- A study by Digiday found that 78% of publishers believe that removing third-party cookies will increase the value of their audience data.
- A Pew Research Center survey found 68% of U.S. adults had already turned off cookies for privacy reasons.
- Apple’s iOS 14.5 update saw a 96% opt-out rate from app tracking, further accelerating the shift toward privacy-first advertising.
For B2B marketers, this means a big change is on the horizon. Personalization, once powered by cookies, is now under threat. Without cookies, targeting specific segments based on browsing history and behavior becomes much more challenging. The need for businesses to rethink their ad strategies and embrace cookieless alternatives has never been more pressing.
In this blog, we’ll break down the pros and cons of various cookieless solutions, like Google Topics API, first-party data, and more. We’ll look at how these changes affect your ability to reach the right customers and what challenges might come up as you transition away from cookies.
10 Best Cookieless Solutions for Marketers
Tired of cookie restrictions getting in the way of your marketing efforts? Here are 10 cookieless solutions that can help you keep targeting and personalizing without relying on third-party cookies.
1. First-Party Data
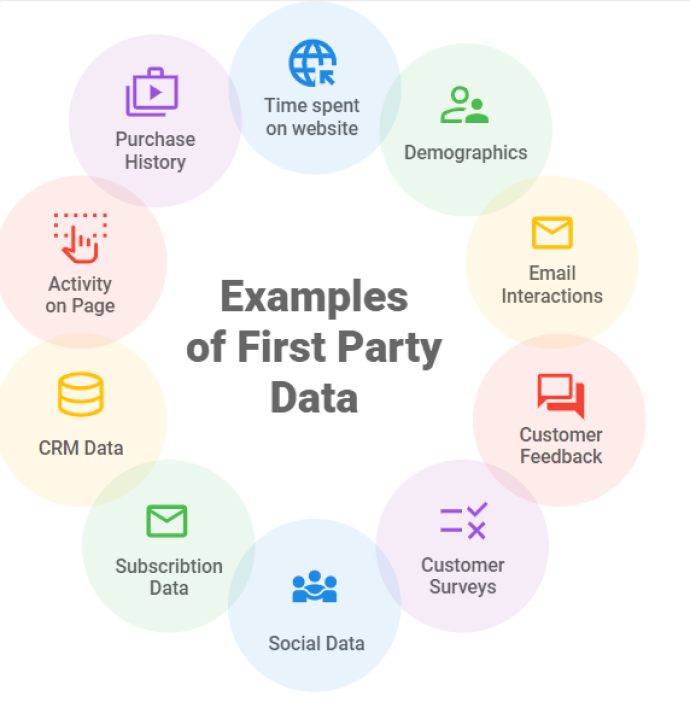
First-party data is information you collect directly from your customers, whether it’s through website visits, email signups, or even in-store purchases. With cookies becoming less reliable, this type of data is gaining more attention because it’s privacy-compliant and tends to be more accurate than third-party data.
Pros:
- Reduces third-party dependence: You no longer have to rely on third-party data providers or cookies to track user behavior. First-party data is all yours, and that means you’re in control of how it’s used.
- Personalized insights: Since the data comes directly from your customers, it’s often more relevant and actionable. You can segment your audience better and create highly targeted campaigns based on actual behaviors and preferences.
- Higher accuracy: First-party data is more reliable because it’s collected from people who have already interacted with your brand. This means fewer inaccuracies and a clearer picture of your audience.
Cons:
- Resource-intensive: Gathering and managing first-party data takes time and effort. You need to set up the right systems for collecting, storing, and analyzing the data, which can be resource-heavy, especially for smaller businesses.
- Implementation challenges: It’s not just about collecting data; you also need the tools and expertise to turn it into actionable insights. Integrating first-party data into your advertising strategy can be tricky if you don’t have the right tech stack or team to handle it.
While first-party data offers a solid foundation for privacy-friendly advertising, managing and utilizing it effectively can be a complex task. That’s where platforms like CustomerLabs 1PD Ops comes in—helping you streamline the collection, management, and analysis of first-party data, so you can unlock its full potential without the hassle.
2. Google Topics API (Formely FLOC)
With the shift towards cookieless advertising, Google has introduced the Topics API as a new way for advertisers to target users without relying on third-party cookies. Rather than tracking individual browsing history, the Topics API groups users into broad categories based on their interests, providing a more privacy-conscious approach to digital advertising. Let’s break down what makes this system work—and where it might fall short.
Pros:
- Simplicity: The Topics API makes it easier for advertisers to set up targeting without the complexity of managing cookies or user tracking. It’s a more streamlined solution that simplifies the targeting process.
- Privacy-safe targeting: With cookies being phased out, privacy is a huge concern. The Topics API ensures user data stays protected by categorizing interests instead of collecting detailed personal information, making it a more secure way to reach your audience.
- User control: One of the best parts of the Topics API is that users have control over the topics they’re associated with. They can view, manage, and even opt out of certain topics if they want to, giving them a say in how their data is used.
Cons:
- Limited topics: For greater privacy, API only uses a set number of predefined topics, which can limit how precisely you can target your audience. If you’re looking for niche or hyper-targeted segments, this might not be granular enough.
- Potential CPA increase: With broader targeting, your cost-per-acquisition (CPA) could rise. Ads may reach users who are interested in a topic but are not likely to convert, driving up costs.
- Adoption uncertainties: Not all advertisers or platforms have fully embraced the Topics API yet, and it could take time before it’s widely adopted across the industry, which might create challenges for marketers who want to use it right away.
3. FLEDGE API
The FLEDGE API is Google’s solution for re-targeting users in a privacy-friendly way. It’s part of the Privacy Sandbox initiative, designed to help advertisers run effective campaigns without relying on third-party cookies.
Pros:
- Privacy-safe re-targeting: FLEDGE lets you target users who’ve shown interest in your products before, but without invading their privacy. It uses aggregated data rather than individual user tracking, keeping things more anonymous.
- Advertiser profile control: As an advertiser, you have control over the audience you’re targeting, but without needing to rely on intrusive cookies or third-party data. You’re still able to refine your audience and boost campaign relevance, just more securely.
Cons:
- Low opt-in rates: Since FLEDGE relies on user consent for tracking, opt-in rates can be a hurdle. Not every user will be willing to opt-in, which can limit the effectiveness of your campaigns.
- Lack of vendor momentum: While Google is pushing FLEDGE, not all ad tech vendors are on board yet. This means there’s still some uncertainty around how widely it will be adopted across the industry, and that could affect how effective it is in the long run.
In short, FLEDGE has potential, but it’s still evolving. While it’s promising for privacy-conscious re-targeting, it might not be the perfect solution for every advertiser—especially with the challenges around adoption.
4. Contextual Advertising
As the advertising world moves away from cookies, contextual advertising is making a strong comeback. Instead of tracking user behavior across sites, it targets users based on the content they’re actively engaging with by using AI to analyze on-page content, URLs, and meta information in real time to understand the context and deliver relevant ads.
For example, if someone’s reading an article about running, they might see an ad for athletic shoes. This approach is not only a privacy-friendly alternative to cookie-based ads but also a way to keep ads relevant without invasive tracking.
Pros:
- Privacy-Friendly: Since contextual ads don’t rely on tracking individual user behavior or collecting personal data, they align well with privacy regulations like GDPR. Users won’t feel like they’re being watched, which builds trust.
- Setup Simplicity: Compared to more complex cookieless solutions, setting up a contextual advertising campaign is relatively simpler. You don’t need to worry about managing data from multiple sources or sophisticated audience-building techniques.
Cons:
- Competitive Costs: Because contextual targeting often relies on premium placements in high-traffic content areas, it can come with a hefty price tag. If you’re competing for those top spots, your costs might increase significantly.
- Potential Disruptiveness: Contextual ads can sometimes feel out of place if they’re not aligned perfectly with the content. If the ad is too off-topic, it can disrupt the user experience and feel like an intrusive interruption.
5. User Identity Graphs
User identity graphs help advertisers track and connect data across different touchpoints to create a complete, unified view of a user. Instead of relying on cookies, these graphs link together customer information from multiple sources—like email, social media, or website interactions—to build detailed profiles. This allows businesses to personalize their marketing in real time, even when cookies are no longer an option.
Pros:
- Handles Complex Journeys: User identity graphs excel at tracking users across different devices and platforms, making it easier to understand the full customer journey. Whether they switch from mobile to desktop or bounce between apps, you can still connect the dots.
- Real-Time Personalization: With a clearer view of who your customers are and how they behave, you can personalize experiences in the moment, delivering relevant content or ads instantly based on real-time behavior.
Cons:
- Privacy Concerns: Since identity graphs link a lot of personal data, there are privacy risks involved. Users may feel uncomfortable with how much information is being collected, especially if they don’t fully understand how their data is being used.
- Transparency Issues: Some identity graph providers might not fully disclose how they collect or use the data, leading to trust issues. This lack of transparency can make both consumers and businesses hesitant to fully embrace the technology.
6. Digital Fingerprinting
Digital fingerprinting is a method that helps advertisers track users without relying on cookies. Instead of storing information in a cookie, it looks at details like a user’s device type, browser settings, and even their location to create a unique “fingerprint.” This lets advertisers identify users across websites without tracking their every move.
Pros:
- Accurate Tracking: Digital fingerprinting can be very accurate. Since it uses several different details about a user’s device, it’s harder to fake or block compared to cookies, making it a more reliable way to identify users.
- Better Targeting: With more accurate data, advertisers can create better, more personalized ads based on real user preferences.
- No Cookies Needed: Since it doesn’t rely on cookies, fingerprinting is a solution that works well in today’s privacy-first environment and is more likely to comply with laws like GDPR.
Cons:
- Privacy Concerns: Even though it doesn’t use cookies, digital fingerprinting can still feel invasive to users, especially if they don’t know it’s happening.
- Browser Blockages: Some browsers, like Safari and Firefox, are blocking fingerprinting methods, just as they’ve done with cookies, which could limit its effectiveness.
- Lack of Transparency: Users often don’t know when their data is being collected for fingerprinting, making it harder for them to opt out or manage their privacy.
7. AI and Machine Learning
AI and machine learning are making huge waves in the world of advertising because these technologies have the potential to transform how we track performance and optimize ad campaigns—without relying on the usual cookie-based tracking methods.
By analyzing vast amounts of data, AI can predict customer behavior and adjust strategies in real time. However, as promising as it sounds, there’s still a lot to figure out, especially when it comes to implementation.
Pros:
- Cookieless Attribution: AI and machine learning use data from first-party sources (like your website or app) and analyze customer behavior in aggregate to give you insights into which ads are driving conversions without violating privacy laws.
- Improved Media Effectiveness: AI can process massive amounts of data to optimize ad placements in real time and identify patterns that humans might miss, leading to smarter ad spend and better ROI.
Cons:
- Requires a Mindset Shift: Switching to AI-powered strategies requires a shift in how you think about advertising. There’s a learning curve when it comes to adapting to a world where everything is powered by algorithms rather than human decision-making. If you’re used to traditional cookie-based methods, it might take time to understand how AI works and how to trust its insights.
- Learning Curve: Implementing AI tools can be complicated. It’s not a “set it and forget it” situation. You’ll need to invest time in training your team, understanding the data AI provides, and fine-tuning your strategies. Hence, the initial setup can feel overwhelming.
In short, AI and machine learning offer a smart, privacy-friendly solution to cookieless advertising, but there’s no denying the initial challenges that come with adopting these tools.
8. Cohort-Based Targeting
Cohort-based targeting is a strategy where instead of targeting individual users, you group them into segments or cohorts based on shared characteristics or behaviors. These could be things like age, interests, location, or past interactions with your brand.
Rather than tracking every individual’s actions, you focus on reaching entire groups of users who share similar traits or patterns. This method aligns well with privacy-first strategies, as it avoids the need for individual-level tracking while still offering effective, personalized marketing.
Pros:
- Better Privacy Compliance: Since you’re targeting groups, not individuals, cohort-based targeting aligns with privacy regulations and minimizes the risk of violating data protection laws.
- Less Reliant on Cookies: It reduces your dependency on third-party cookies, making it a great alternative as the industry moves toward a cookieless future.
- Scalable: Once you identify key cohorts, you can easily scale your campaigns to reach a large number of users who match those characteristics.
- Targeting based on Behavior: You can segment cohorts based on actions or behaviors, allowing you to craft more relevant and tailored campaigns.
- Improved Campaign Efficiency: By focusing on cohorts, you can create ads that resonate more with groups of users, rather than relying on a one-size-fits-all approach, which usually boosts campaign performance.
Cons:
- Lack of Granularity: Cohorts are broad, so you might lose some granularity in your targeting compared to hyper-focused individual targeting.
- Potentially Overbroad Segments: If your cohorts are too large, you could end up with less relevant audiences, which may decrease the effectiveness of your campaigns.
- Initial Setup Effort: Identifying the right cohorts and setting up the right segmentation can take time and effort, especially if you don’t have robust data or tools in place.
- Less Personalization: Cohort-based targeting might not offer the same level of personalized experience that individual targeting provides, especially if the cohorts are too broad.
Cohort-based targeting offers a nice balance between privacy and personalization, making it a good fit for the future of digital marketing. However, like any strategy, it comes with its own challenges—primarily around making sure your cohorts are specific enough to drive meaningful results.
9. Data Clean Rooms
As privacy regulations tighten and third-party data becomes less reliable, data clean rooms have emerged as a game-changer for marketers looking to collaborate with other brands without violating privacy rules. In simple terms, a data clean room is a secure environment where multiple parties can share and analyze their data without exposing any sensitive or personally identifiable information (PII).
These platforms let you combine first-party data from different sources to generate insights, but in a way that ensures privacy remains intact. Think of it as a controlled space where brands can work together while keeping their customers’ data safe. Despite their high cost, DCRs are widely used.
Pros:
- Privacy-compliant data sharing: Data clean rooms enable brands to collaborate on data-driven insights without compromising user privacy. All data is anonymized and aggregated, keeping sensitive information safe.
- Stronger partnerships: They allow businesses to share insights across organizations without sharing raw data. This can strengthen relationships between partners, opening the door for new opportunities.
- Data analysis without exposure: You get to combine data from multiple sources (e.g., advertisers, publishers, etc.) and gain valuable insights, without any of the risks associated with exposing raw customer data.
- Better audience insights: By combining multiple data sets, you can uncover richer insights about your target audiences, improving segmentation and campaign targeting.
- Fewer data silos: Data clean rooms help eliminate silos by unifying information across different systems, allowing for more comprehensive analysis and decision-making.
Cons:
- Complex setup: Setting up and integrating a data clean room can be a bit tricky. It requires specific technology and expertise, which can be a hurdle for businesses that are new to the concept.
- Limited access to raw data: While you can analyze insights, you don’t have direct access to the raw data. This can limit how granular your analysis can get.
- Costs: Some clean room platforms can be expensive, particularly for smaller businesses or those just getting started with data-driven marketing.
- Limited control: Depending on the platform you use, you may not have full control over how data is processed or shared. This can be a concern if you have specific security or privacy needs.
- Dependence on external platforms: You’re relying on third-party providers to handle the data clean room setup, which can lead to concerns about data governance and trust.
Data clean rooms are not a one-size-fits-all solution, but they’re certainly worth considering if you want to collaborate with partners while keeping privacy at the forefront.
10. Intent Data
Intent data gives you insights into what potential customers are interested in and how likely they are to make a purchase. It tracks actions like website visits, content consumption, searches, and interactions that suggest a person is “in the market” for something. Unlike basic demographic data, intent data shows intent – whether a person is actively considering a product or service, making it more powerful for marketers.
Pros:
- Better targeting: Intent data helps you identify hot leads. Instead of casting a wide net, you can focus your efforts on people who are actively interested in your product, increasing the likelihood of conversion.
- Increased relevancy: With intent data, you can tailor your marketing messages to meet the specific needs of prospects. If someone’s been researching a certain product or service, you can serve them relevant ads or content at the right time.
- Shorter sales cycles: When you know someone’s intent, you can quickly engage them with targeted campaigns, speeding up the sales process. This reduces the time it takes to convert prospects into customers.
- Stronger leads: Intent data gives you insights into where prospects are in their buyer journey. This helps you prioritize your leads, focusing more on those who are closer to making a decision.
Cons:
- Privacy concerns: Intent data relies on tracking user behavior, and this can raise privacy issues. With tighter regulations like GDPR, you’ll need to make sure you’re collecting and using data responsibly.
- Data overload: Collecting intent data from multiple sources can lead to an overwhelming amount of information. Without the right tools or strategy, it’s easy to get lost in the data and miss key insights.
- Accuracy can vary: Not all intent signals are equal. Some actions, like a person visiting a product page, don’t always indicate strong buying intent. You’ll need to refine your approach to identify the most meaningful signals.
Intent data is an excellent way to focus your marketing efforts on the right people at the right time. However, it’s crucial to balance its power with ethical data practices and the right tools effectively.
Now that you understand the pros and cons of different cookieless advertising solutions let’s better understand why you should consider making the switch.
Why You Should Move to Cookieless, First-Party Data In 2024
As privacy regulations tighten and cookies become less reliable, the future of digital marketing lies in first-party data. Unlike third-party data, which relies on external sources and cookies, first-party data is fully under your control. It’s more reliable, privacy-compliant, and offers deeper insights into your customers’ needs and preferences.
A study found that businesses using first-party data for key marketing functions saw up to a 2.9X increase in revenue and a 1.5X boost in cost savings.
But making the switch to a cookieless, first-party data strategy can feel overwhelming. However, incorporating robust platforms like CustomerLabs which has a powerful suite of tools, can help your business. To make the most of your first-party data without the need for cookies or invasive tracking methods.
Here’s how:
Seamless Data Collection:
CustomerLabs captures real-time customer data directly from your website, app, and other owned channels. This eliminates the need for third-party cookies and ensures all data is privacy-compliant.
Create Rich Customer Profiles:
With CustomerLabs, you can build detailed customer profiles that reflect real behavior and intent. This allows you to create highly personalized experiences for each user, improving engagement and conversions.
Cross-Channel Insights:
CustomerLabs integrates your first-party data across all touchpoints, giving you a unified view of your customers. Whether they’re browsing your website, interacting with your app, or responding to emails. This helps you deliver consistent messaging and better-targeted campaigns without relying on cookie-based tracking.
Better Attribution and ROI:
By using first-party data, you can track the true impact of your campaigns without worrying about cookie-based attribution issues. CustomerLabs helps you accurately attribute conversions and optimize your ad spend so you get more value from every dollar.
Switching to a cookieless, first-party data strategy future-proofs your marketing efforts and helps you gain more control over your data. With CustomerLabs, you can make this transition smoothly, ensuring your campaigns are both effective and privacy-friendly.
Conclusion
As cookies phase out, businesses need to adapt and explore cookieless solutions to stay competitive. Privacy concerns and new regulations are pushing the shift away from cookie-based tracking, making it crucial for marketers to find alternative ways to reach customers.
Options like first-party data, contextual advertising, and new APIs can help fill the gap, but each comes with its own challenges. Understanding these solutions and their limitations is key to navigating the future of advertising. While the benefits—better privacy and compliance—are clear, you may face trade-offs like a steeper learning curve or less precise targeting. If you’re looking for a straightforward, privacy-first solution, CustomerLabs 1PD Ops can help you move beyond cookies while keeping your targeting and personalization on track.







