In an era where customer-centricity drives business success, Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) have emerged as transformative tools for the banking sector. A CDP enables banks to unify customer data from multiple sources, providing a comprehensive view of customer behaviors and needs. This capability is particularly valuable in banking, where understanding customer preferences and ensuring secure data handling are essential for building trust and delivering personalized services.
In this article, we will explore how CDPs help banks streamline operations, enhance customer engagement, and meet compliance requirements, while highlighting the role of CustomerLabs in empowering financial institutions to achieve these goals.
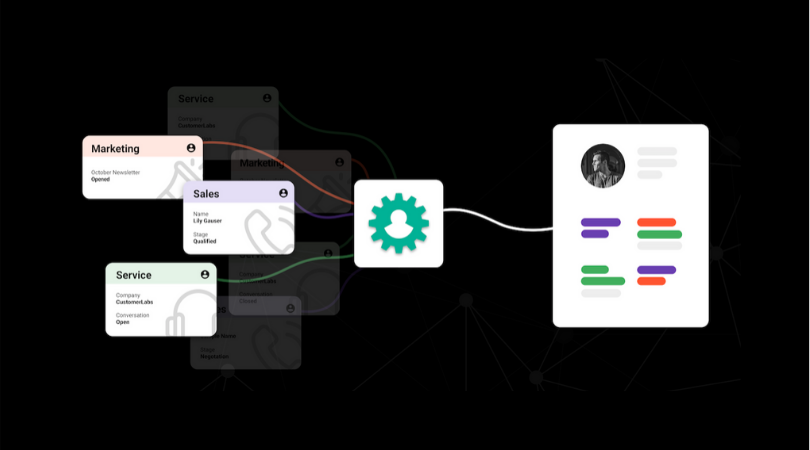
How CDPs Streamline and Unify Customer Data Management ?
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are central to modern marketing strategies, enabling businesses to collect, unify, and leverage customer data effectively. By creating detailed, unified profiles, CDPs help deliver personalized, cross-channel experiences that drive engagement and improve ROI. These platforms not only streamline data management but also empower businesses to target their “ideal customers” and expand their audience reach.
Core Functions of CDPs:
- Data Collection
CDPs consolidate data from various sources, such as CRM systems, websites, and marketing tools, into a single hub, ensuring a unified view of each customer. - Identity Resolution
They connect data points across devices and channels, linking known identifiers with anonymous data to map complete customer journeys. - Data Activation
Unified profiles enable real-time personalization by integrating with platforms like email automation, analytics tools, and content management systems. - Insight Generation
CDPs provide actionable insights through segmentation, lookalike audience creation, and analytics, enabling businesses to refine their strategies and measure ROI.
In essence, Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) help marketers extend their reach by identifying the “perfect” customers and finding new audiences that match their profiles, optimizing efforts, and enhancing ROI. This unified approach empowers teams to stay data-driven while delivering exceptional customer experiences.
Also read on: CDP or Data Warehouse: What are the Key Differences?
Unlike other marketing technologies, which often focus on specific functions like email marketing or advertising, CDPs provide a comprehensive, centralized view of customer data from various sources, enabling marketers to create more personalized and effective strategies across all channels. This holistic perspective sets CDPs apart from tools that operate in silos.
Importance of CDPs in Banking Sector
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) allows banks to create a unified, real-time view of customer and prospect data by integrating multiple data sources, including third-party inputs. With a CDP, banks can break down silos of fragmented customer data and create a single, comprehensive “golden record” that is free from inconsistencies, ensuring accurate and accessible data for better customer insights.
For banks, this means having an up-to-date and comprehensive customer profile at every touchpoint, allowing marketing, sales, and customer service teams to offer personalized and relevant interactions. With a CDP, banks can:
- Integrate CRM and transactional data to build a primary customer list.
- Enrich this list with digital engagement data from sources like web tracking tools, email, and mobile apps.
- Enhance profiles with second- and third-party data to predict customer intent and personalize interactions.
- Seamlessly connect adtech and martech tools to transform anonymous visitors into known customers.
By leveraging the rich data insights provided by a CDP, banks can improve conversion rates, boost cross-selling opportunities, enhance customer loyalty, and drive a stronger net promoter score (NPS).
Also read on: Top Benefits of Using a Customer Data Platform
With this foundational understanding of CDPs, let’s dive deeper into how these platforms help banks break down data silos.
Breaking Down Data Silos in Banking
Data silos have long been a challenge for the banking industry. Banks often manage data across multiple channels—online banking, physical branches, mobile apps, and third-party services—which can lead to fragmented insights and missed opportunities for personalized engagement.
Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) are revolutionizing this aspect by breaking down data silos and creating a unified view of the customer.
1. Consolidating Data from Various Sources
A CDP integrates data from all customer touchpoints, including transactional data, customer behavior, and interactions across various devices and platforms. This unified data structure allows banks to gather a 360-degree view of the customer, improving personalization and optimizing customer experience strategies.
For instance, a customer may access their bank account via mobile, but might also visit a branch for an in-person consultation. A CDP can merge these separate data points, enabling the bank to provide a more informed and seamless experience, whether the customer is online or offline.
- Omnichannel Integration: CDPs consolidate customer data from both physical and digital channels, ensuring that customers receive consistent and personalized service regardless of how they interact with the bank.
- Enhanced Customer Segmentation: By consolidating all data, banks can create more accurate customer segments and tailor their marketing efforts to match specific customer needs, such as targeting individuals interested in home loans or credit card products.
2. Securing Sensitive Financial Data
Banks handle some of the most sensitive customer data, from financial transactions to personally identifiable information (PII). Ensuring this data remains secure and compliant with privacy regulations is of utmost importance. CDPs not only aggregate data but also incorporate stringent security measures, including encryption and role-based access controls, to protect customer information from breaches and unauthorized access.
Creating a Singular Customer View
Understanding the complete profile of each customer is essential for driving personalized engagement and improving service offerings. A Singular Customer View (SCV) consolidates data from various sources into a unified profile, allowing banks to deliver more tailored experiences and meet customer expectations more effectively.
1. Integrating Demographic, Behavioral, and Transactional Data
In the modern banking environment, it’s not enough to simply know a customer’s name or address. A truly effective customer data platform integrates demographic, transactional, and behavioral data to provide a complete picture of the customer. This comprehensive view enables banks to better understand customer preferences, anticipate future needs, and enhance overall satisfaction.
- Demographic Data: Basic customer details such as age, income, location, and marital status.
- Behavioral Data: Information about how a customer interacts with the bank, such as usage patterns on mobile banking, browsing history on financial products, and responses to marketing offers.
- Transactional Data: Detailed information about the customer’s financial activities, including deposits, withdrawals, loans, and credit card usage.
By synthesizing this data into a unified customer profile, banks can provide hyper-personalized offerings, such as offering tailored financial products, customized recommendations, and personalized financial advice.
2. Facilitating Personalized Marketing and Engagement
Once data is integrated into a CDP, it enables banks to design highly targeted marketing campaigns and deliver relevant content at the right time. By combining insights from behavioral and transactional data, banks can personalize product recommendations, credit offers, and financial advice for customers based on their unique needs and preferences.
Actionable Insights Through Predictive Analytics
This section focuses on how predictive analytics within CDPs helps banks understand customer behavior and make data-driven decisions to improve engagement. By leveraging real-time data processing, banks can offer proactive, personalized experiences that drive customer satisfaction and business outcomes.
1. Understanding Customer Behavior and Preferences
CDPs utilize advanced analytics to understand and predict customer behavior. Banks can leverage these insights to create more effective engagement strategies and deliver products and services that match customers’ evolving needs.
- Customer Churn Prediction: By analyzing historical data, banks can identify early warning signs of customer churn and take proactive steps to retain at-risk customers, such as offering personalized incentives or reaching out with targeted retention campaigns.
- Product Purchase Likelihood: CDPs help banks predict the likelihood of customers purchasing additional products, such as loans, credit cards, or insurance, based on past behavior and preferences.
2. Real-Time Data Processing
CDPs also facilitate real-time data processing, enabling banks to engage customers proactively. For instance, if a customer applies for a loan online, the bank can immediately offer them tailored financial advice or personalized offers, improving the customer experience and increasing conversion rates. Real-time processing also supports quicker decision-making, which is critical in the fast-paced financial sector.
As we’ve explored predictive analytics, it’s time to examine how banks can enhance personalization in their interactions with customers through CDPs.
Enhancing Personalization in Banking
Personalization has become a cornerstone of modern banking, and customer data platforms (CDPs) play a pivotal role in delivering tailored experiences. By leveraging customer insights and predictive analytics, banks can create personalized interactions that meet the unique needs of each customer. This section explores the key ways CDPs help enhance personalization, from omnichannel journeys to predictive analytics, ultimately driving customer satisfaction and loyalty.
1. Omnichannel Customer Journeys
A key feature of modern banking is the ability to engage with customers across multiple channels—whether it’s through a mobile app, in-branch visit, or website. A CDP integrates these interactions into one seamless journey, ensuring that customers receive personalized service no matter where or how they engage.
- Cross-Channel Personalization: For example, if a customer inquires about a mortgage via the mobile app, a bank using a CDP can use the same information to offer tailored mortgage products when they visit the branch or interact with the bank’s website.
- Consistent Customer Experience: Banks can ensure customers have a consistent experience across all touchpoints, leading to higher satisfaction and increased brand loyalty.
3. Predictive Analytics for Churn, Purchases, and Risk
Predictive analytics is a powerful tool for banks to enhance decision-making by forecasting customer behavior. By leveraging data insights, banks can proactively manage customer retention, cross-selling opportunities, and risk mitigation, ultimately improving operational efficiency and customer satisfaction. Below are key areas where predictive analytics plays a crucial role:
- Customer Churn Prediction: By analyzing trends, banks can identify at-risk customers and implement retention strategies, such as personalized offers or loyalty programs.
- Product Purchase Likelihood: Banks can predict the likelihood of customers purchasing additional products, enhancing cross-selling opportunities.
- Risk Mitigation: Predictive analytics also helps in assessing high-risk borrowers, supporting better lending decisions.
3. Targeted Marketing and Customized Offers
CDPs enable banks to send targeted marketing messages based on detailed customer profiles. Banks can deliver personalized offers, such as a custom loan rate or a promotional savings plan, tailored to each individual’s financial situation. By focusing on what customers truly need, banks can significantly improve engagement and conversion rates.
Now that we’ve discussed personalization, let’s explore how CDPs help banks maintain compliance and ensure data security.
Compliance and Data Security in Banking
In the banking industry, maintaining compliance with regulatory requirements and safeguarding sensitive customer data is paramount. Customer data platforms (CDPs) play a crucial role in helping banks meet these demands by providing secure, transparent, and compliant data management solutions.
Let’s discuss how CDPs help with regulatory compliance and data security, particularly around managing first-party data and maintaining privacy standards.
1. Regulatory Compliance
Banks must navigate a complex regulatory environment that includes regulations such as KYC (Know Your Customer), AML (Anti-Money Laundering), and GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation). A CDP helps banks stay compliant by ensuring that data collection, storage, and access are secure and transparent.
- Automated Compliance Reporting: CDPs track and log data access, ensuring that banks can provide detailed audit trails when required for regulatory purposes.
- Privacy and Consent Management: CDPs can also manage customer consent preferences, ensuring that data usage complies with privacy regulations.
2. First-Party Data Management
Managing first-party data securely is essential in today’s regulatory landscape. CDPs ensure that banks can collect, store, and process customer data while safeguarding privacy. By maintaining robust data security protocols, banks can protect sensitive information, preventing breaches and unauthorized access.
With the compliance and security mechanisms in place, let’s now examine some of the challenges banks may face when implementing CDPs and the solutions that can overcome them.
Implementation Challenges and Solutions
When implementing a Customer Data Platform (CDP), banks often encounter several hurdles. These challenges can include integrating CDPs with legacy systems, transitioning from traditional data management platforms, and ensuring seamless collaboration between departments. However, by leveraging modern solutions, these obstacles can be overcome, allowing banks to unlock the full potential of their data.
1. Overcoming Legacy Systems
A significant challenge banks face when adopting a Customer Data Platform (CDP) is the integration with legacy systems. Many financial institutions still rely on outdated infrastructure that can make it difficult to fully embrace new technologies. The process of connecting old systems with modern CDPs often requires a complex, time-consuming overhaul.
CustomerLabs 1PD Ops, a leading provider of AI-powered First-party data Ops, understands the challenges that come with legacy systems. They offer seamless integration solutions, designed to bridge the gap between traditional infrastructures and cutting-edge data management tools. By working with CustomerLabs, banks can continue using their existing systems while upgrading their capabilities for better data-driven customer engagement. This allows for a smoother transition and maximizes the value of their current technology investments.
2. Traditional vs. Modern Data Platforms
Here’s a comparison between traditional data management systems and modern Customer Data Platforms (CDPs), highlighting their key differences and advantages.
| Aspect | Traditional Data Management Systems | Customer Data Platforms (CDPs) |
| Data Handling | Primarily designed for structured data from a single source. | Capable of handling large volumes of structured, semi-structured, and unstructured data from multiple sources. |
| Data Integration | Limited ability to integrate diverse data types and sources. | Integrates data from a wide range of channels and systems (CRM, web, social, etc.). |
| Real-Time Processing | Often batch-oriented, with delayed processing times. | Supports real-time data processing, enabling immediate insights and actions. |
| Scalability | Struggles to scale efficiently with increasing data complexity and volume. | Designed for scalability, capable of adapting to growing data needs without significant performance degradation. |
| Data Access and Personalization | Limited tools for customer segmentation and personalization. | Offers advanced segmentation and personalized experiences based on comprehensive customer profiles. |
| Flexibility and Adaptability | Rigid structure, requiring costly upgrades for changes. | Highly flexible, easily adaptable to changing data sources, regulatory requirements, and business needs. |
By adopting CDPs, banks can not only break free from the constraints of traditional systems but also unlock the ability to drive more personalized and data-driven decision-making, ultimately improving customer satisfaction and operational efficiency.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Customer Data Platforms are essential tools for banks seeking to stay competitive in a rapidly evolving financial landscape. By consolidating customer data, enabling personalization, and improving compliance, CDPs allow banks to create more meaningful customer relationships and enhance operational efficiency.
As banks increasingly rely on data to drive their strategies, it is important to go beyond just a CDP by adopting a 1PD Ops solution like CustomerLabs can offer significant advantages. With its cutting-edge technology, CustomerLabs empowers banks to achieve real-time insights, enhance personalization, and streamline their data management processes. Interested in transforming your bank’s customer engagement strategy? CustomerLabs, the leading provider of AI-powered First-party data Ops platform, specializes in helping businesses harness their customer data to drive personalized marketing, improve customer experiences, and increase ROI.
Reach out to CustomerLabs 1PD Ops today and learn how their innovative Customer Data Platform can help you unlock the true value of your customer data.